

abc music notation is an easy and convenient way of writing and editing music. Here we will look at how we can read, write and edit the abc code to create the music. We also provide a quick reference guide to the commonly used symbols, characters and letters used in abc music notation.
Let us start with an example, here is the start of a well known Irish tune:

And here is the abc code that created this sheet music:
X:10
T: Father O'Flynn
T: Top of the Cork Road
C: Trad.
O: Ireland
R: jig
M: 6/8
L: 1/8
K: Dmaj
|: A | dAF DFA | ded cBA | dcd efg | fdf ecA |
| dAF DFA | ded cBA | dcd efg fdd d2 :|
First we have the header codes, each is a letter followed by a colon.
X: Tune number. Sometimes used for tune library identification
T: The title of the tune, song or piece, this is printed at the top of the music score.
T: A secondary title line often used for alternative tune names, this is printed in small letters under the first title.
C: The composer of the music, if it is traditional put "traditional" or "trad". This is printed under the titles and to the right.
M: The meter of the music such as 6/8 for a jig, 4/4 for a reel and 2/4 for a waltz. C| (note that | is a vertical line not a small L or a large i) can be used for common 4/4 time.
L: The note length as a proportion of a bar such as 1/8 is used for jigs and reels
R: Rythm such as hornpipe, jig, reel, waltz, polka, etc. The better playback programs use this information to add the correct rythm during playback.
K: The key that the tune is in such as D or Dmaj for D major or Edor for E dorian.
IMPORTANT NOTE: The headers X: T: and K: must be included and must be placed in the correct order with X: on the first line, T: on the second line and K: on the last line of the headers.
Other header lines are often used such as:
O: Origin, this will be printed in brackets after the C: entry.
D: Discography, where the music can be found on recordings.
Q: Speed of playback in beats per minute, this may only be needed if you are exporting a midi file. Playback programs allow you to adjust the speed of playback on the fly.
B:
R:
Z: Often used for id code information.
S: Source - commonly used for where the tune was collected from.
I:
H:
Under the headers we type the code for the tune itself.
Here is an example to illustrate what we have covered so far:
X:1
T:Main Title
T:Secondary title or alternative names
C:Composer
O:Yorkshire
M:4/4
Q:160
L:1/8
R:Reel
K:C
|A,B,CD EFGA|Bcde fgab|c'd'e'f' g'a'b'|
And here is what this codewill look like:
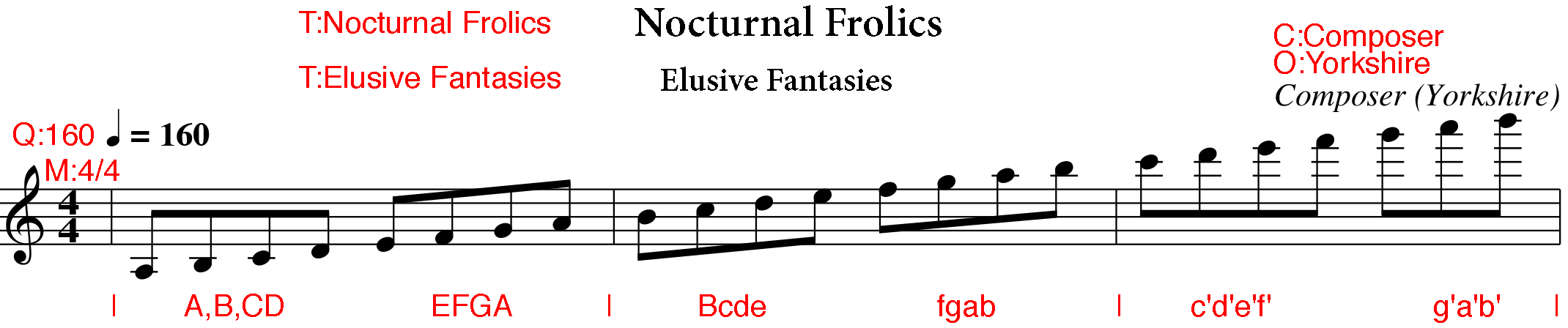
NOTES:
By adding the K: header we set the key, if the key is C then there are no sharps and flats. If the key is a G it has one sharp - the F#, if the key is D then it has 2 sharps the F# and the C#. abc recognises this and will add the sharps and flats for the key at the start of the stave (the line of music). In the same way as when we are reading music, abc will consider every note marked as a sharp or flat at the start of the music as that sharp or flat everytime it occurs in the music.
If we wish to make a note sharp we place a ^ before the note so ^c = C#
To make a note flat we place an underline _ before the note so _e = E ![]()
To make a note natural (cancel out the sharp or flat) we place and equal sign = before the note so =e returns E ![]() to E.
to E.
To add a chord we type the chord in excamation marks immediately before the abc note where the chord starts such as
| "G"gabg gabg | "Em"e
W: is placed after the code for the line of music followed by the words to be inserted.
Here is the abc code for adding chords and words:
X:2
T:Love Will You Marry Me?
M:C|
K:G
|:"G"D2DE GAB2|"C"GE E2 GE E2|"G"D2DE GABc|"D"dedB A2 "G"G2:||
W: - Love - will you - marry me, - marry me, __ marry me, - Love will you mar-ry me and take me out of dan-ger
And here is what it will look like:

| Code | Item | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| X:1 | Number | The number is not important but it is essential that there is an X: number and that it is at the start of the code, abc software recognises the X: as the start of a tune |
| T: | Title | The title of the tune, song or piece, this is printed at the top of the music score. |
| T: | Secondary Title | A secondary title line often used for alternative tune names. |
| C: | Composer | The composer of the music, if it is traditional put "traditional" or "trad". |
| M: | Meter | The meter of the music such as 6/8 for a jig, 4/4 for a reel and 2/4 for a waltz. |